The majority of robots used in manufacturing plants throughout the world are employed by the automotive industry. A new record was reached for the operating stock at nearly 1 million units or almost one-third of the total deployed across all industries, according to research from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
According to IFR president Marina Bill:
“The automotive industry effectively invented automated manufacturing. Today, robots are playing a vital role in enabling this industry’s transition from combustion engines to electric power. Robotic automation helps car manufacturers manage the wholesale changes to long-established manufacturing methods and technologies.”
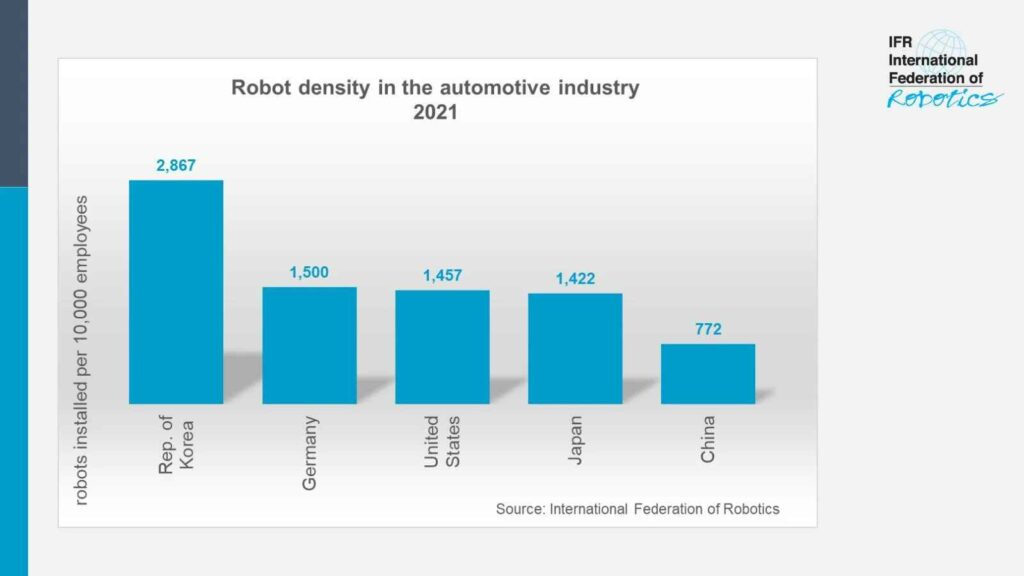
Robot density is a crucial metric for assessing the degree of automation now present in the top car-producing nations. In the Republic of Korea, there were 2,867 industrial robots for every 10,000 workers in 2021. The United States comes in second with 1,457 units, Japan comes in third with 1,422 units, and Germany comes in second with 1,500 units per 10,000 workers.
Related: Autonomous Robots That Can Charge EVs
China, the largest automaker in the world, has a robot density of 772 units but is quickly coming up, according to the IFR. At 61,598 units in 2021, new robot installations in the Chinese automotive industry nearly doubled in just one year. Of the 119,405 units deployed in factories worldwide, this made up 52% of the total.
Politically ambitious goals for electric vehicles are putting financial pressure on the auto industry. By 2035, the European Union intends to stop selling automobiles that contribute to air pollution. By 2030, the U.S. government wants to have a 50% market share for electric vehicle sales, and by 2035, all new cars sold in China must be “new energy” powered. The remaining 50% must be hybrid vehicles, with the other half required to be electric, fuel-cell, or plug-in hybrid vehicles.
Related: Toyota to Convert Engine Plants to Battery Factories
Most automakers that have previously invested in traditional “caged” industrial robots for basic assembly are now investing in collaborative applications for final assembly and finishing activities. Tier-two automotive components suppliers, many of which are SMEs, are taking longer to fully automate. This is projected to change as robots get smaller, more versatile, easier to program, and less capital-intensive.

The IFR published its most recent global robotics study in late 2022. According to the research, 517,385 new industrial robots were installed in factories worldwide in 2021, setting a record for the sector. Robot installations in the year 2021 increased by 31% from the previous year. 2018 saw a 22% increase above the pre-pandemic record for robot installations. Almost 3.5 million units were operational robots at the time the report was issued, setting a new global record.

A computer animation professional with over 23 years of industry experience having served in leading organizations, TV channels & production facilities in Pakistan. An avid car enthusiast and petrolhead with an affection to deliver quality content to help shape opinions. Formerly written for PakWheels as well as major publications including Dawn. Founder of CarSpiritPK.com




